Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
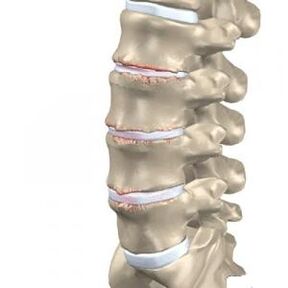
- L1 and L2 - Loss of sensitivity in the "rider's pants" area, i. e. the groin area and inner thighs. If lumbar osteochondrosis is complicated by a hernia, pain may occur in both legs at the same time.
- L5 – Severe pain, decreased sensitivity in the lower back and thumb, and decreased ability to bend the fingers.
- S1 – Severe pain, decreased sensitivity in the outer calves and thighs, pain in the feet from the little toe to the fourth toe. Typically, when this root is damaged, the Achilles tendon and plantar reflexes are lost.
- Damage to the Deproge-Gotteron artery - In the chronic course of osteochondrosis, paralysis of the lower legs and buttocks may occur, and sensitivity in the anogenital area may disappear.
- Simultaneous damage to the L5, S root, and Deproge-Gotteron arteries results in "sciatica paralysis" syndrome, a loss of pelvic and motor function.
Complications of lumbar osteochondrosis
Diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Keep your lower back dry and warm, don't overcool your spine, and avoid drafts.
- Do not lift heavy objects or carry them over long distances.
- Try not to make sudden movements.
- Maintain correct posture while working and resting.
- Change your position as often as possible and try not to stay in one position for too long.
- Get physical therapy.
- Try not to stay in a bent position for long periods of time.
- When cleaning, use a long mop, broom, and vacuum cleaner with a long hose so you don't have to bend down.
- To lift correctly: Bend at the waist and straighten your back, or bend your knees and straighten your back to pick up the bag and stand up straight. Keep the loaded hand as close to the body as possible.
- If you need to bend down to pick something up from the floor (such as a table or under a bed), kneel on one knee and keep your back straight.
- Distribute the weight evenly between your hands.
- Strengthen your hip muscles, stretch your spine, and take a walk every day.
- Balance your diet and enrich it with dairy and plant products.
- Stick to the drinking habit - 1. 5-2 liters of water and herbal tea per day.
- Break bad habits - drinking, smoking, drugs.